Objectives |
Resources |
|
• How and why the birth of the cattle industry led to the era of the American cowboy and new patterns of migration and settlement in the southwestern United States.
• How and why aridity, availability of land and new land laws influenced the westward migration and settlement of various groups, such as homesteaders and “sodbusters”. • How American Indians were pushed to the Great Plains and forced to settle on reservations. • How the development of the railroad and telegraph industry impacted patterns of western migration and settlement during the 19th Century. • How and why southern African American “Exodusters” moved westward after the collapse of Reconstruction in the South. • How westward settlement and expansion impacted various ethnic groups during the 19thCentury (e.g., Asians, Hispanics and American Indians). • How and to what extent the “Americanization” of American Indian led to the break up of reservations and the disintegration of American Indian culture at the dawn of the 20th Century. • How westward settlement and expansion impacted the roles of women, their contributions and relationships. • How and why the federal government adopted a policy of “Americanization” or assimilation of American Indians and the impact of the policy on American Indians and the nation. • How and why conflicting claims over land and water rights led to violent “range wars” between ranchers and farmers in the southwestern United States. • How westward settlement and expansion led to the Indian Wars of the Great Plains that culminated at the Battle of Wounded Knee. How African American freedom presented limited opportunities for upward mobility and movement out of the South during the 19th Century (e.g., American Colonization Society, “Exodusters” and Wilmington Race Riots). • How and to what extent westward migration and the “Americanization” of the American Indian led to the break up of reservations and the disintegration of • American Indian culture at the dawn of the 20th Century. • How and why the federal government encouraged the westward growth of the railroad industry and how the industry’s growth and movement impacted the settlement, daily lives and fortunes of various groups • How westward migration and Manifest Destiny impacted perceptions of the frontier and the “American Dream” (e.g., Frederick Jackson Turner and “The Significance of the Frontier in American History”, Helen Hunt Jackson and A Century of Dishonor, Frank Norris and The Octopus). • How American Indians viewed the westward migration of American settlers, their own movement to reservations, as well as, government and public attempts at “Americanization” (e.g., Simon Pokagon and “The Future of the Red Man,” Chief Joseph, Zitkala-Sa). • How and why American Indians were forced to the Great Plains and eventually reservations by the mid 19th Century and how that movement impacted American Indian culture. • How, why and to what extent American innovations immediately after the Civil War led to economic development and settlement of the frontier (e.g., barbed wire, farm implements, air brakes and steam turbines). • To what extent westward movement and settlement of various groups fulfilled or denied the promises of freedom and prosperity along the frontier (e.g., American Indians, women, homesteaders, Mormons and missionaries). (Individual rights, individual responsibility, equal justice under the law, private property rights Homestead Act Morrill Act homesteaders soddies Dawes Act Bozeman Trail Comstock Lode Wounded Knee Little Big Horn Black Hills Sand Creek Massacre Chisholm Trail Promontory, Utah (golden spike) Transcontinental Railroad Exoduster Migration Barbed wire John Deere steel plow windmill McCormick mechanical reaper Refrigerated Rail Car Railway Air Brake assimilation ethnogenocide open range range war Americanization Helen Hunt Jackson/Century of Dishonor buffalo role of women on Great Plains Frederick Jackson Turner/Frontier Thesis sodbusters reservations Sitting Bull Ghost Dance Movement Mormons/Great Salt Lake settlement Sears & Roebuck Chicago/railhub/slaugherhouses Found on Newspapers.com
Blacks of the Old West
Exodus to Kansas The 1880 Senate Investigation of the Beginnings of the African American Migration from the South Bio of Pap Singleton Exoduster primary source doc 1 Exoduster primary source doc 2 Exoduster primary source doc 3 Exoduster primary source doc 4 Exoduster primary source doc 5 Exoduster primary source doc 6 Exoduster primary source doc 7 Exoduster primary source doc 8 Voorhees Committee Report part 1 Voorhees Committee Report part 2 Voorhees Committee Report part 3 |
Bury My Heart at Wounded Knee questions
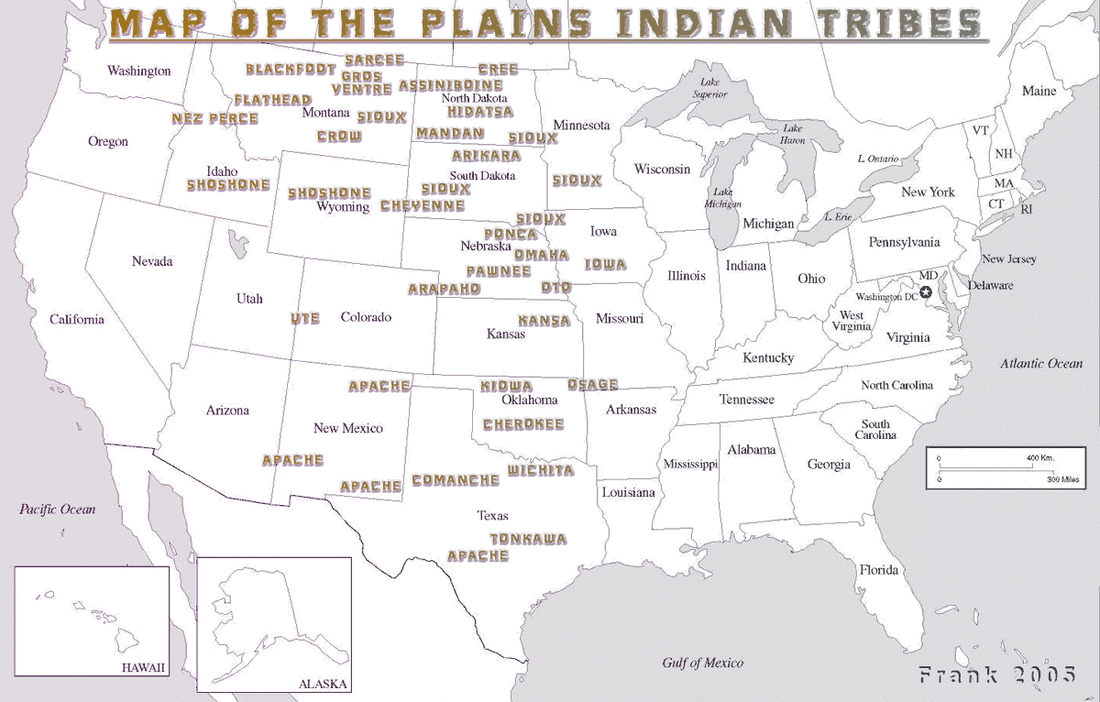
Guided Reading Sand Creek Massacre lesson (primary source docs) West Worksheets Dawes Act Lesson Map for Above West Map Activity
outline map for above Brochure Activity LOC Lesson Indian Boarding Schools LOC Lesson American Indian Reservation Controversies
|